Implementation
This chapter explains how the wallets are organised and protected.
File layouts
The data is organized in 4K blocks. The first block is a header block used to store various information to identify the storage files. Other blocks have a clear 16-byte header and an HMAC-256 signature at the end. Blocks are encrypted either by using the master key, the directory key, the data key or a per-data fragment key.
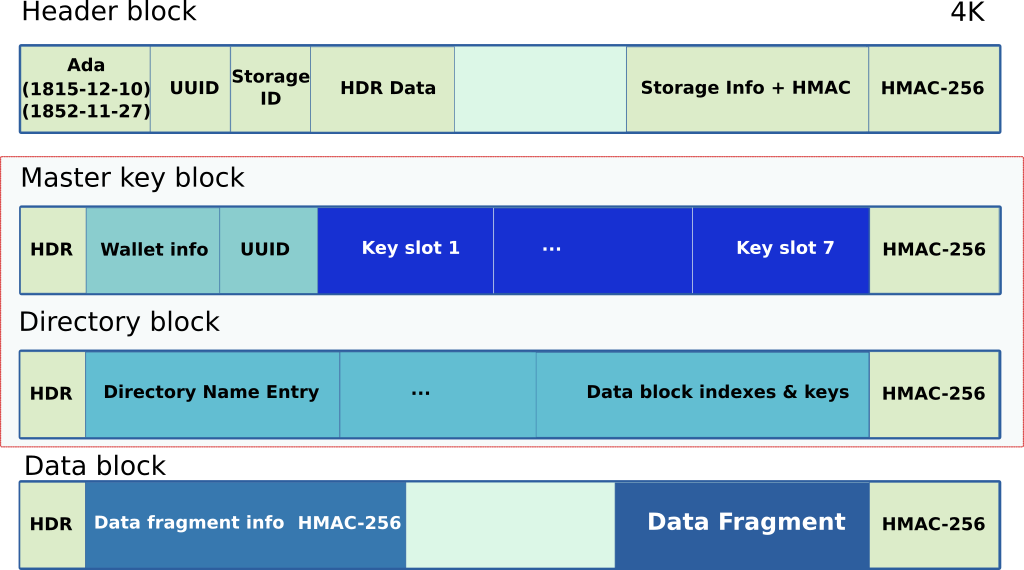
The master key block and directory block are the two blocks that contain encryption keys.
Header block
The first block of the file is the keystore header block which contains clear information signed by an HMAC header. The header block contains the keystore UUID as well as a short description of each storage data file. It also contains some optional header data.
+------------------+
| 41 64 61 00 | 4b = Ada
| 00 9A 72 57 | 4b = 10/12/1815
| 01 9D B1 AC | 4b = 27/11/1852
| 00 01 | 2b = Version 1
| 00 01 | 2b = File header length in blocks
+------------------+
| Keystore UUID | 16b
| Storage ID | 4b
| Block size | 4b
| Storage count | 4b
| Header Data count| 2b
+------------------+-----
| Header Data size | 2b
| Header Data type | 2b = 0 (NONE), 1 (GPG1) 2, (GPG2)
+------------------+
| Header Data | Nb
+------------------+-----
| ... |
+------------------+-----
| 0 |
+------------------+-----
| ... |
+------------------+-----
| Storage ID | 4b
| Storage type | 2b
| Storage status | 2b 00 = open, Ada = sealed
| Storage max bloc | 4b
| Storage HMAC | 32b = 44b
+------------------+----
| Header HMAC-256 | 32b
+------------------+----
GPG Header data
The GPG encrypted data contains the following information:
+------------------+-----
| TAG | 4b
+------------------+-----
| Lock Key | 32b
| Lock IV | 16b
| Wallet Key | 32b
| Wallet IV | 16b
| Wallet Sign | 32b
+------------------+-----
Master keys
Wallet header encrypted with the parent wallet id
+------------------+
| 01 01 | 2b
| Encrypt size | 2b
| Parent Wallet id | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
+------------------+
| Wallet magic | 4b
| Wallet version | 4b
| Wallet lid | 4b
| Wallet block ID | 4b
+------------------+
| Wallet gid | 16b
+------------------+
| Wallet key count | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
+------------------+
| Key type | 4b
| Key size | 4b
| Counter for key | 4b
| Counter for iv | 4b
| Salt for key | 32b
| Salt for iv | 32b
| Key slot sign | 32b
| Dir key # 1 | 32b ---
| Dir iv # 1 | 16b ^
| Dir sign # 1 | 32b |
| Data key # 1 | 32b |
| Data iv # 1 | 16b | Encrypted by user's password
| Data sign #1 | 32b |
| Key key # 1 | 32b |
| Key iv # 1 | 16b v
| Key sign #1 | 32b ---
| Slot HMAC-256 | 32b
| PAD 0 / Random | 80b
+------------------+
| Key slot #2 | 512b
+------------------+
| Key slot #3 | 512b
+------------------+
| Key slot #4 | 512b
+------------------+
| Key slot #5 | 512b
+------------------+
| Key slot #6 | 512b
+------------------+
| Key slot #7 | 512b
+------------------+
| PAD 0 / Random |
+------------------+
| Block HMAC-256 | 32b
+------------------+
Directory Entries
The wallet repository block is encrypted with the wallet directory key.
+------------------+
| 02 02 | 2b
| Encrypt size | 2b = BT_DATA_LENGTH
| Wallet id | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
+------------------+
| Next block ID | 4b Block number for next repository block with same storage
| Data key offset | 2b Starts at IO.Block_Index'Last, decreasing
+------------------+
| Entry ID | 4b ^
| Entry type | 2b | = T_STRING, T_BINARY
| Name size | 2b |
| Name | Nb | DATA_NAME_ENTRY_SIZE + Name'Length
| Create date | 8b |
| Update date | 8b |
| Entry size | 8b v
+------------------+
| Entry ID | 4b ^
| Entry type | 2b | = T_WALLET
| Name size | 2b |
| Name | Nb | DATA_NAME_ENTRY_SIZE + Name'Length
| Create date | 8b |
| Update date | 8b |
| Wallet lid | 4b |
| Wallet master ID | 4b v
+------------------+
| ... |
+------------------+--
| 0 0 0 0 | 4b (End of name entry list = DATA_KEY_SEPARATOR)
+------------------+--
| ... | (random or zero)
+------------------+-- <- = Data key offset
| ... |
+------------------+
| Storage ID | 4b ^ Repeats "Data key count" times
| Data block ID | 4b |
| Data size | 2b | DATA_KEY_ENTRY_SIZE = 58b
| Content IV | 16b |
| Content key | 32b v
+------------------+
| Entry ID | 4b ^
| Data key count | 2b | DATA_KEY_HEADER_SIZE = 10b
| Data offset | 4b v
+------------------+
| Block HMAC-256 | 32b
+------------------+--
Data Block
Data block start is encrypted with wallet data key, data fragments are encrypted with their own key. Loading and saving data blocks occurs exclusively from the workers package. The data block can be stored in a separate file so that the wallet repository and its keys are separate from the data blocks.
+------------------+
| 03 03 | 2b
| Encrypt size | 2b = DATA_ENTRY_SIZE * Nb data fragment
| Wallet id | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
| PAD 0 | 4b
+------------------+-----
| Entry ID | 4b Encrypted with wallet id
| Slot size | 2b
| 0 0 | 2b
| Data offset | 8b
| Content HMAC-256 | 32b => 48b = DATA_ENTRY_SIZE
+------------------+
| ... |
+------------------+-----
| ... |
+------------------+
| Data content | Encrypted with data entry key
+------------------+-----
| Block HMAC-256 | 32b
+------------------+
Keystore Protections
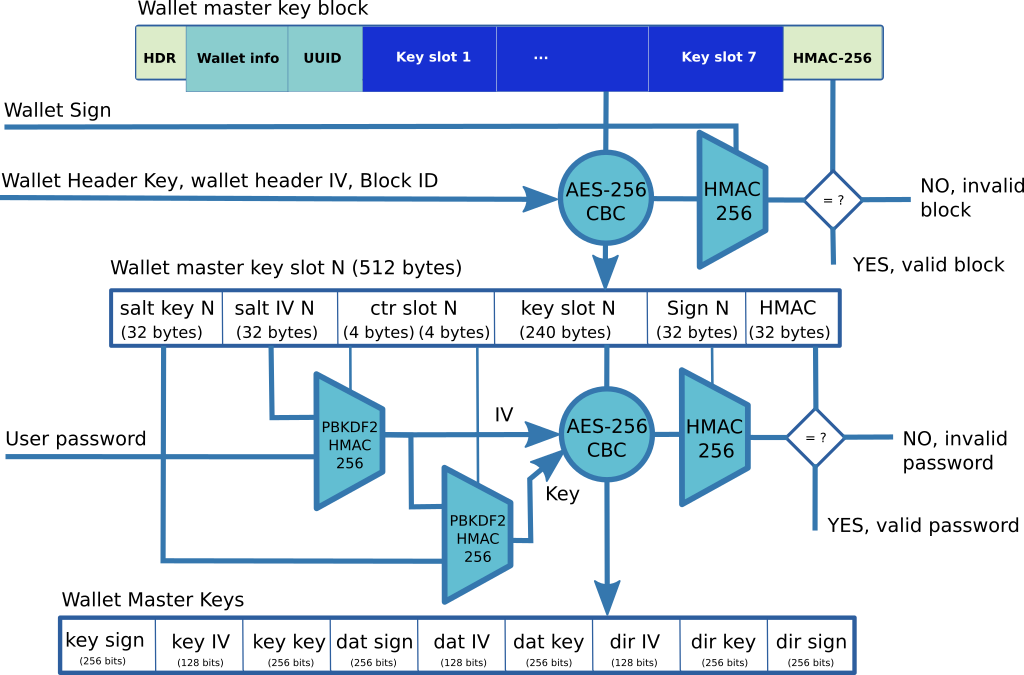
The master key block contains the primary keys that are used to encrypt other blocks. The master key block contains 7 key slots that are capable to unlock the master keys. Each slot is independent and can be associated with a specific authentication method. Two authentication methods are supported:
- password based authentication,
- GPG based authentication.
Password Protection
In this mode, three secret information must be provided:
- the wallet header key and IV,
- the wallet signature key,
- the user password.
First, the wallet master key block is decrypted with AES-256-CBC by using the wallet header key and IV. The HMAC-256 signature is then computed with the wallet signature key on the decrypted content and the clear 16-byte header at beginning of the block. The HMAC signature must match the signature found at end of the block.
Once the wallet master key block is decrypted, the user password is checked against the available key slots. For a given password protected key slot, a derived key is generated by using the PBKDF2-HMAC256 algorithm. First, a 16-byte IV is generated and then a 32-byte key is generated. For each PBKDF2 execution a specific 32-byte salt and counter is used. The key slot is then decrypted by using the derived keys with AES-256-CBC. An HMAC-256 signature is built to verify the decrypted content. When the HMAC signature matches the signature found in the key slot, the provided user's password is valid.
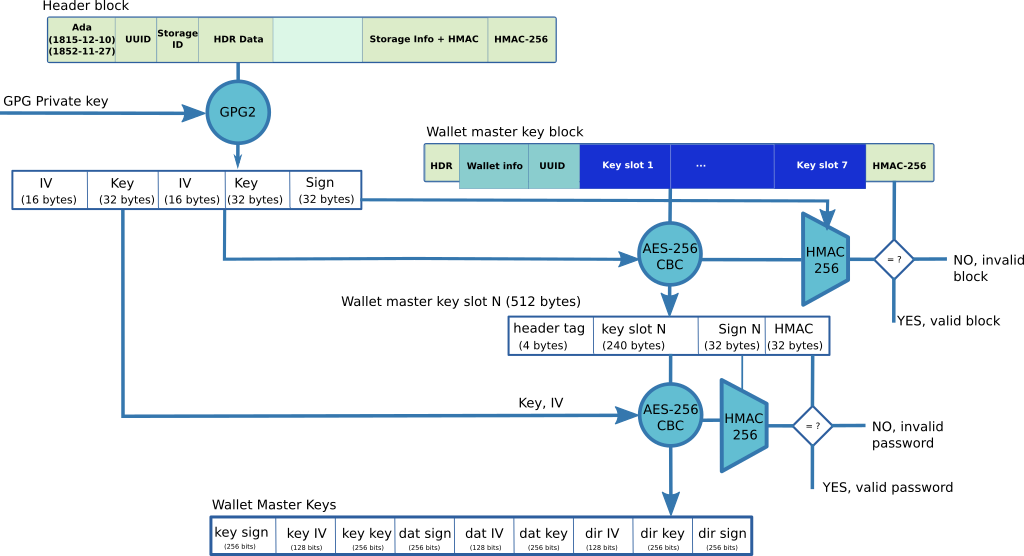
GPG Protection
With the GPG protection, the header block contains additional information that is decrypted with the user's GPG private key. When such additional data is successfully decrypted, it contains several parts:
- the wallet header key and IV,
- the wallet signature key,
- the key slot encryption key and IV.
The wallet master key block is decrypted and validated using the same process as the password protection.
The key slot that matches the GPG key is identified by a header tag that is found in the key slot and in the GPG header data. The key slot is decrypted by using the key slot encryption key and IV that was decrypted by GPG. It is validated using HMAC-256.
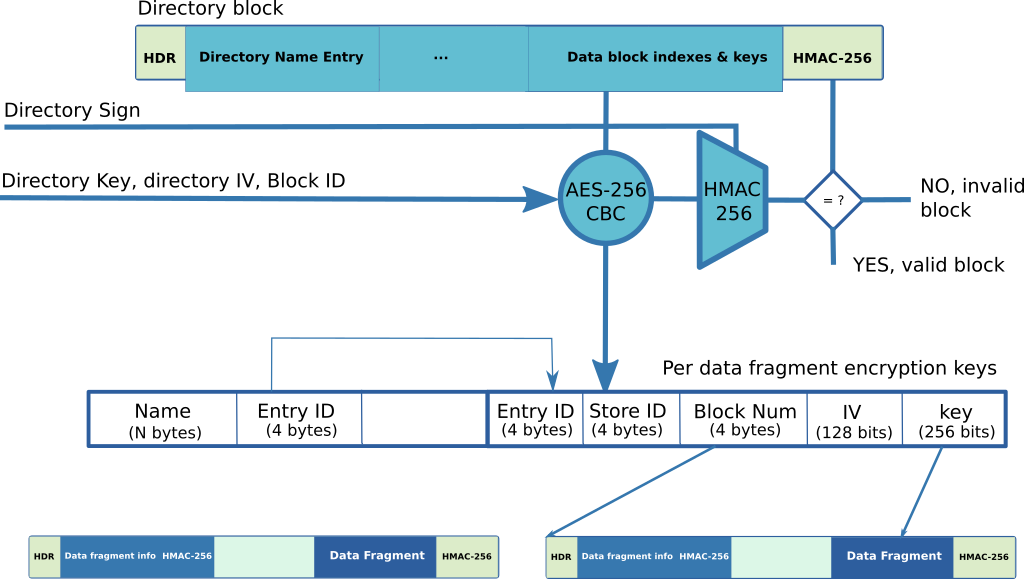
Directory Protection
A directory block contains the name of contents found in the keystore as well as the keys used to encrypt data fragments. The directory block is decrypted with AES-256-CBC by using the directory key and IV. The directory block number is xored on the directory IV to obtain the IV used for the decryption. An HMAC-256 signature is computed with the clear 16-byte header and the decrypted directory content. It is then verified against the block HMAC.
Once decrypted, the directory block contains two areas. At beginning of the block, it contains the entry names that are stored in the keystore. For each entry, a unique entry ID is assigned and is used as a unique reference.
At end of the block, it contains the encryption keys and the block numbers where the data fragments are stored. Each data fragment has its own encryption key and IV.